Lattice Structure – Optimize Your 3D Printed Parts
Additive manufacturing brings a whole new world of opportunities and changes in manufacturable parts by creating new possibilities in free form design. For example, the creation of lattice structures. A lattice is made of repeated unit cells. Lattices can be uniform i.e. exact same cell is repeated in all directions, or variable i.e. the size or spacing of the cells is different in different directions.

Lattice Structure
The lattice structure possesses many superior properties to conventional structures. With AM technology the lattice structures are made by adding material layer-by-layer directly from a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model, rather than the conventional processes with complicated procedures. The lattice structures have demonstrated excellent architectural, mechanical and functional flexibilities. The AM lattice structure blurs the boundary between material and structure, and is able to integrate more than one function into a physical part, providing practical solutions to a wide range of applications like aerospace, automotive fields, fabricating biomedical parts and many more.
Designing of lattice structures
For designing of lattice structures several important points are to be considered:
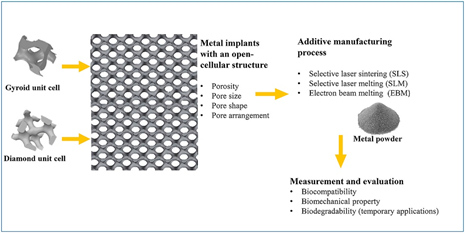
Designing of lattice structures
- Cell structure: The list of cell structures is very long and ever-growing. The most common cell structures include cubic, star, hexagonal, diamond, octet and tetrahedron etc.. These cells are repeated or mixed to get the desired application for your system. Some structures are more efficient (higher stiffness-to-weight ratios), others dampen energy better, and some are a little more aesthetically pleasing.
- Cell size and density: Cell size refer to the size of an individual unit cell and density refers to how many cells are repeated within a space. The cell size depends on the thickness and length of its members and connecting nodes. Larger cells can be easier to print but can also act stiffer; likewise, smaller cells allow for more homogeneous system responses but are limited by feature sizes.
- Material selection: Your chosen material can define which lattice properties are possible. Elastomeric or soft materials generally require a smaller and denser cell population to reduce sag during printing. Alternatively, lattices printed with a more rigid material generally allow a greater design range with thinner members and larger cell sizes.
- Cell orientation: The angle a cell is printed at can affect the success of a print because it influences the amount and placement of supports required. A well-chosen and oriented lattice is self-supporting, which does not require separate supports. Oftentimes, a structure can be rotated to reduce supports.
With 3D printing, lattices bring many advantages to your applications like:
- High strength to weight ratio: Through latticing we are able to remove material in the non-critical as well as critical areas of part without compromising with the part functionality. Although latticing does reduce the overall strength of the part, the weight savings can improve this strength-to-weight ratio.
High strength to weight ratio
- High surface area: Lattice increases the amount of surface area available in a same volume. This benefit makes them suitable for application like heat transfer and chemical reactions by increasing efficiency.
- High shock absorption: Lattices also helps in protecting products from drops or collisions by absorbing impact energy. Lattices can either be integrated into a product like hip implants to reduce impact stresses or used as a sacrificial feature to protect the critical components of a product.
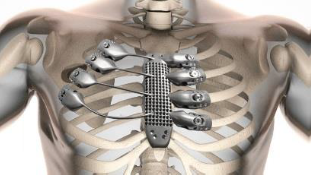
High shock absorption
CONCLUSION
With metal 3D printing, lattices bring many advantages. They reduce the mass and weight of the object which implies less material used and a lower price. Indeed, the solid material structure is replaced by the lattice structure sections which reduces the amount of material used in the 3D printed structure. In the additive manufacturing sector, the less material used to create a part equals to a lower price. Thus lattices have huge application in Medical implants, Automotive Components and Aerospace and Aeronautic Components.
By..
Abhishek Kushwaha