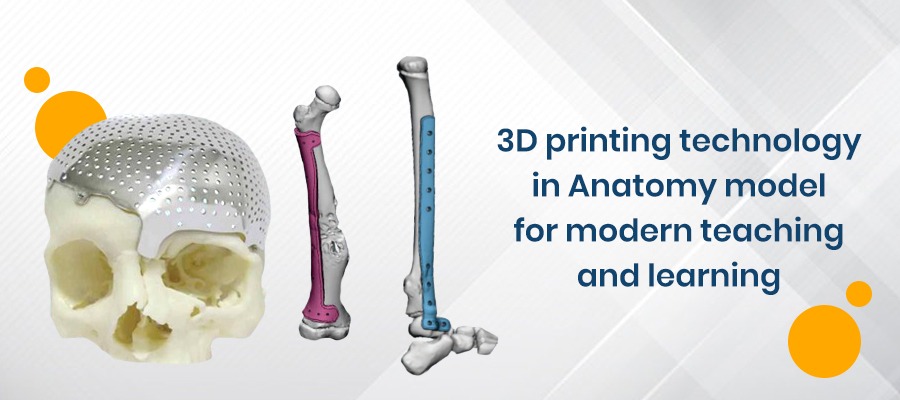
In teaching anatomy, three-dimensional 3D printed models have grown in popularity as an alternative to the traditional approach of cadaveric dissection. It has the advantage of being less expensive and more repeatable. It is widely utilized in postgraduate education, although its effectiveness in undergraduate education has not been thoroughly investigated.
At 3D Incredible, we believe every patient is important and every patient deserves special treatment. That’s why we provide patient-specific implants and services to assist a surgeon to the individual patient in the best way possible.
Metal 3D printing (Additive Manufacturing) is the latest manufacturing technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way metal parts are being manufactured traditionally. It has the capability of developing very complex and intricate shapes without tooling.
Benefits:
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is the transformation of a three-dimensional (3D) computer model into a real object. The “printed materials” are built layer by layer under computer control until the physical thing fits the blueprint on the computer. Durable nylon, gypsum, aluminum, textile materials, and polylactic acid are all common 3D printing materials. 3D printing provides the following advantages over other tissue engineering scaffolds and rapid prototyping technology: high accuracy, good integration, fast rebuilding, and low cost. Furthermore, 3D model can aid in the understanding of complicated physical structures and the printing of difficult-to-find models.
These models can help patients understand their sickness, improve their doctor-patient connection, and have more faith in the treatment process. They also provide supplemental education to patients, including information about normal and abnormal body structures, which helps to improve doctor-patient relationships.
It is possible to create high-fidelity model of cardiac defects with this technology. These models teach students about the heart and increase their enthusiasm for studying. They can also be replicated in huge numbers, giving trainees models to learn from and practice their abilities with. In comparison to traditional plastic models, 3D printed models are more flexible and robust. Furthermore, 3D printing has a low cost of production, produces an exact anatomical structure, and displays normal or pathological structural changes.
The fundamental learning object for a medical student used to be a genuine human body. Anatomical maps are presented in several surgical teaching and research departments in hospitals to help students learn. Some departments now use 3D computer visuals to teach students about Human Anatomy.
3D printing, on the other hand, provides the advantages of high precision, good integration, quick rebuilding, and low cost. Gradually, technology has made its way into the medical classroom. It will be highly valuable for practice and teaching purposes to employ 3D printing technology to construct an anatomical tailored model to fully comprehend the anatomical relationship between lesions and complicated surrounding systems.
Application
Three-dimensional printing can be used in a variety of fields, including space science, technology, and medicine. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography scans, for example, can be used to scan the human body. It can then use many layers of resin to simulate human structures. Resin is applied in layers, resulting in solid objects. It’s a potentially game-changing device that can help with surgical education and clinical practice. For example, preoperative patient counselling, surgical planning, and training can all benefit from the 3D printing of cerebral arteriovenous malformation models.
Residents are trained in anatomy via three-dimensional printing. In fields like an autopsy, plasticization, computer simulation, and anatomical modeling and imaging, this technology has shown significant promise as a teaching tool. 3D printing has been used in the teaching of anatomy to medical students in recent decades.
Conclusion:
It is expected that 3D printing will become more widely integrated into undergraduate anatomy instruction, as well as in the assessment of anatomical knowledge and clinical skill training. The creation of an online 3D model database could make it easier for educators to create models for specific instructional reasons. Thus, 3D metal printed implant/printing seems to play a significant role in the global healthcare sector, especially in orthopaedic surgery. Many medical professionals predict that 3D printing technology will drastically change orthopaedic surgery for the better.