Introduction to FDM 3D printing

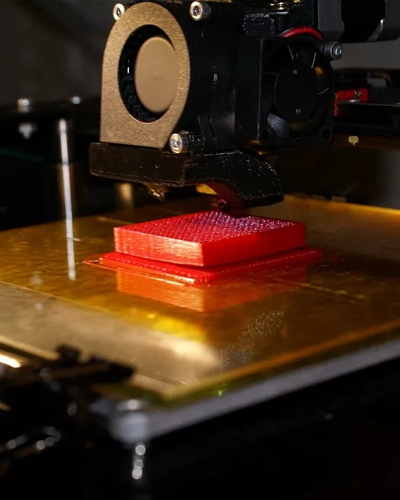
Fused Deposition Modelling, or FDM, is an additive manufacturing technique that involves the extrusion of materials through a nozzle and their subsequent joining to form three-dimensional structures.
During FDM 3d printing, a heated nozzle in a 3D printer melts polymer-based filament, causing it to be deposited on the build platform in two-dimensional layers. Finally, these layers, when they are still warm, fuse to form a three-dimensional part.
The additive nature of FDM and its soluble support material make it easier to create objects with intricate internal voids and geometries.
Benefits of FDM 3D Printing
It has several benefits. These include:
- Large range of materials High-performance materials blended with fibres, such as PLA, PET, PA, ABS, and PC
- Easy media removal
- Lack of post-curation Ability to produce extremely huge chunks without distortions
- Combining materials during manufacture is possible.
Applications of FDM 3D Printing
Machines that use fused deposition modelling (FDM) make it easier to produce high-quality parts using permitted materials. Several industries, including aerospace, medical, and manufacturing, use this additive technology. Among its uses are the following ones:
- Models for product functional and dimensional validation
- The potential for chromating ABS components
- Manufacturing of low-volume items
- Production of less expensive parts
Achievable Feature Size:

Pros & Cons

| Feature | FDM |
| Maximum Build Volume | 1000x1000x1000 mm |
| Wall thickness | 1mm |
| Holes | 2mm |
| Surface Finish | Rough |
| Accuracy | 0.5 |
| Material | ABS , PLA |
| Mechanically | Strong and flexible |
Pros
- FastLow-cost consumer machines and materials
Cons
- Low accuracy
- Low details
- Limited design compatibility

